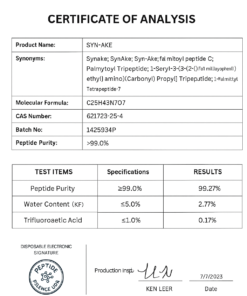
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD⁺) is a coenzyme found in all living cells and plays a central role in cellular metabolism and bioenergetics. It exists in two primary forms—oxidized (NAD⁺) and reduced (NADH)—acting as a critical electron transporter in redox reactions. NAD⁺ is essential for the function of various enzyme classes, particularly those involved in oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis, and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle.
Additionally, NAD⁺ serves as a substrate for key enzymatic processes, including sirtuin-mediated deacetylation and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)-dependent DNA repair pathways. These functions position NAD⁺ as a molecule of interest in studies involving aging, cellular resilience, and metabolic function
Be the first to review “NAD+ 1000MG” Cancel reply
Related products
Peptide
Rated 5.00 out of 5
$130.00
Peptide
Rated 4.80 out of 5
$46.00 – $149.00
Peptide
Rated 4.80 out of 5
$48.00
Peptide
Rated 5.00 out of 5
$85.00
Peptide
$40.71
Peptide
$50.00
Peptide
Rated 5.00 out of 5
$65.00
Peptide
$200.00

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.